Read the JAWS ARIA Support Notes and Key Concepts
Support legend
 means we have found this feature to be implemented interoperably (across multiple browsers)
means we have found this feature to be implemented interoperably (across multiple browsers)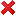 means we have found that this feature is not implemented
means we have found that this feature is not implemented- ? means we are unsure whether this feature is supported, this may be due to lack of testing or lack of clarity around what 'support' of this feature is supposed to convey to the user.
JAWS testing - In progress
| Role | Description | Test case | Interaction | Supported | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
alert
|
A type of live region with important,
and usually time-sensitive, information.
See related alertDialog and status.
|
 |
This role does not appear in either the virtual buffer or Forms Mode, but its contents are spoken by JAWS when an alert is made visible. |
||
alertdialog
|
A type of dialog that contains an alert message, where initial focus goes to an element within the dialog. See related alert and dialog.
|
 |
|||
application
|
A structure containing one or more focusable elements requiring user input, such as keyboard or gesture events, that do not follow a standard interaction pattern supported by a widget role. - (changed) | application test |  |
||
article
|
A section of a page that consists of a composition that forms an independent part of a document, page, or site. | article test |
|
 |
|
banner
|
A region that contains mostly site-oriented content, rather than page-specific content. |
|
 |
||
button
|
An input that allows for user-triggered actions when clicked or pressed. See related link.
|
 |
|||
checkbox
|
A checkable input that has three possible values: true, false, or mixed. |
|
 |
||
cell
|
A cell in a tabular container. |
|
 |
||
columnheader
|
A cell containing header information for a column. |  |
|||
combobox
|
A presentation of a select; usually similar to a textbox where users can type ahead to select an option, or type to enter arbitrary text as a new item in the list. See related listbox.
|
|
 |
||
complementary
|
A supporting section of the document, designed to be complementary to the main content at a similar level in the DOM hierarchy, but remains meaningful when separated from the main content. |
|
 |
||
contentinfo
|
A large perceivable region that contains information about the parent document. |
|
 |
||
definition
|
A definition of a term or concept. | definition test |  |
||
dialog
|
A dialog is an application window that is designed to interrupt the current processing of an application in order to prompt the user to enter information or require a response. See related alerTDialog.
|
 |
Note (Aug 31, 2017): When tested with JAWS 18 & IE 11, dialog not announced when opened. Additionally, field names/labels shared across all input fields. JAWS 18 & FF 55 worked as expected.
|
||
directory
|
A list of references to members of a group, such as a static table of contents. |
See Table of Contents |
 |
Note (Sept 19, 2017): tested with JAWS 18 and FF, expected list commands to navigate to role=directory, does not occur. | |
document
|
A region containing related information that is declared as document content, as opposed to a web application. | document test |  |
|
|
feed
|
A scrollable list of articles where scrolling may cause articles to be added to or removed from either end of the list. | feed test |  |
||
figure
|
A perceivable section of content that typically contains a graphical document, images, code snippets, or example text. | figure test |  |
||
form
|
A landmark region that contains a collection of items and objects that, as a whole, combine to create a form. See related search.
|
|
 |
Need to check whether it needs an accessible name to be announced/navigable | |
grid
|
A grid is an interactive control which contains cells of tabular data arranged in rows and columns, like a table.
|
 |
|||
gridcell
|
A cell in a grid or treegrid.
|
 |
|||
group
|
A set of user interface objects which are not intended to be included in a page summary or table of contents by assistive technologies. | ? |
|
||
heading
|
A heading for a section of the page.
|
|
 |
Requires aria-level attribute with a valid value to announce level.
|
|
img
|
A container for a collection of elements that form an image. | img test |
|
 |
|
link
|
An interactive reference to an internal or external resource that, when activated, causes the user agent to navigate to that resource. See related button.
|
|
 |
Need to check if visited/unvisited state exposed, expect not as this comes from native link implementation. | |
list
|
A group of non-interactive list items. See related listbox.
|
|
 |
||
listbox
|
A widget that allows the user to select one or more items from a list of choices. See related combobox and list.
|
 |
|||
listitem
|
A single item in a list or directory.
|
|
 |
||
log
|
A type of live region where new information is added in meaningful order and old information may disappear. See related marquee.
|
log test |  |
|
|
main
|
The main content of a document. |
|
 |
||
marquee
|
A type of live region where non-essential information changes frequently. See related log.
|
? | |||
math
|
Content that represents a mathematical expression. | ? | |||
menu
|
A type of widget that offers a list of choices to the user. |
|
 |
||
menubar
|
A presentation of menu that usually remains visible and is usually presented horizontally.
|
 |
|||
menuitem
|
An option in a group of choices contained by a
menu or menubar.
|
|
 |
||
menuitemcheckbox
|
A checkable menuitem that has three possible values:
true, false, or mixed.
|
? | |||
menuitemradio
|
A checkable menuitem in a group of
menuitemradio roles, only one of which
can be checked at a time. |
? | |||
navigation
|
A collection of navigational elements (usually links) for navigating the document or related documents. |
|
 |
||
none
|
An element whose implicit native role semantics will not be mapped to the accessibility API. See synonym presentation. | ? | |||
note
|
A section whose content is parenthetic or ancillary to the main content of the resource. |
|
 |
|
|
option
|
A selectable item in a select list. |  |
|||
presentation
|
An element whose implicit native role semantics will not be mapped to the accessibility API. | presentation test |  |
||
progressbar
|
An element that displays the progress status for tasks that take a long time. |  |
|||
radio
|
A checkable input in a group of radio roles, only one of which can be checked at a time.
|
"radio button checked/not checked" label content "x of y" where x = position in radio group, y = number of radio buttons in group. |
|
 |
|
radiogroup
|
A group of radio buttons. | ? | |||
region
|
A large perceivable section of a web page or document, that the author feels is important enough to be included in a page summary or table of contents, for example, an area of the page containing live sporting event statistics. |
If the region has an accessible name then:
|
 |
||
row
|
A row of cells in a tabular container. |
|
 |
||
rowgroup
|
A group containing one or more row elements in a grid. | rowgroup test |  |
Need to test with rowgroup+accessible name | |
rowheader
|
A cell containing header information for a row in a grid. |  |
|||
scrollbar
|
A graphical object that controls the scrolling of content within a viewing area, regardless of whether the content is fully displayed within the viewing area. | scrollbar test | ? | ||
search
|
A landmark region that contains a collection of items and objects that, as a whole, combine to create a search facility. See related form .
|
|
 |
||
searchbox
|
A type of textbox intended for specifying search criteria. | searchbox test |
|
||
separator
|
A divider that separates and distinguishes sections of content or groups of menuitems. |
(When using JAWS, start at heading "Example," then read down) |
|
 |
|
slider
|
A user input where the user selects a value from within a given range. |
If the
|
 |
||
spinbutton
|
A form of range that expects the user to select from among discrete choices. |
If the spinbutton has the appropriate scripted event handlers:
|
 |
|
|
status
|
A container whose content is advisory information for the user but is not important enough to justify an alert, often but not necessarily presented as a status bar. See related alert.
|
? | |||
switch
|
A type of checkbox that represents on/off values, as opposed to checked/unchecked values. |
|
? | ||
tab
|
A grouping label providing a mechanism for selecting the tab content that is to be rendered to the user. |  |
|||
table
|
A section containing data arranged in rows and columns. The table role is intended for tabular containers which are not interactive. |
|
 |
||
tablist
|
A list of tab elements, which are references
to tabpanel elements.
|
? | |||
tabpanel
|
A container for the resources associated with a tab, where each tab is contained in a tablist.
|
? | |||
term
|
A word or phrase with a corresponding definition. See related definition. | term test |  |
||
textbox
|
Input that allows free-form text as its value. | textbox test |
|
 |
|
timer
|
A type of live region containing a numerical counter which indicates an amount of elapsed time from a start point, or the time remaining until an end point. | ? | |||
toolbar
|
A collection of commonly used function buttons represented in compact visual form. |  |
|
||
tooltip |
A contextual popup that displays a description for an element. |  |
|
||
tree
|
A type of list that may contain sub-level nested groups that can be collapsed and expanded. |  |
|
||
treegrid
|
A grid whose rows can be expanded and collapsed in the same manner as for a tree. | ? | |||
treeitem
|
An option item of a tree. This is an element within a tree that may be expanded or collapsed if it contains a sub-level group of treeitems.
|
 |
ARIA States
| State | Description | Test case | Interaction | Supported | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
aria-busy |
Indicates an element is being modified | aria-busy testcase |
In Firefox & Chrome, an element marked as aria-busy is omitted from the accessibility tree for the page. Does not work in IE11. Content cannot be navigated to or interacted with when |
||
aria-checked |
Indicates the checked state of an element |
|
|||
aria-current |
Indicates an element is the current item in a collection | test-cases.tink.uk/aria-current | All tokens supported in Chrome, Firefox, and IE | ||
aria-disabled |
Indicates an element is perceivable but disabled | test-cases.tink.uk/aria-disabled | Element reported as "unavailable" in Chrome, Firefox, and IE
|
||
aria-expanded |
Indicates the current expansion state of an element | test-cases.tink.uk/aria-expanded | Element reported as "expanded" or "collapsed" in Chrome and Firefox, but not IE | ||
aria-grabbed |
Indicates an element's grabbed state in a drag and drop operation | Deprecated in ARIA 1.1 | |||
aria-hidden |
Indicates whether an element is exposed to the accessibility API | test-cases.tink.uk/aria-hidden | Element hidden in Chrome, Firefox, and IE Note: this Firefox bug |
||
aria-invalid |
Indicates the entered data does not conform to the expected format |
 |
|||
aria-pressed |
Indicates the current pressed state of an element | Element announced as "pressed" in Firefox, but not IE. Also triggers forms mode under ceratin circumstances. Refer to issue: Use of aria-pressed triggers manual forms mode | |||
aria-selected |
Indicates the current selected state of an element |
|
Works on certain roles and elements, needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
| State |
ARIA Properties
| Property | Description | Test case | Interaction | Supported | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
aria-activedescendant |
Identifies the currently active element when DOM focus is on a composite widdget, textbox, group, or application |
|
|||
aria-atomic |
Indicates whether ATs will present all or part of changes in a live region |
|
Works on certain roles and elements, needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-autocomplete |
Indicates whether the element has autocomplete capability | ? | |||
aria-colcount |
Defines the total number of columns in a table | ? | |||
aria-colindex |
Defines an element's column index, or position with respect to the total columns in a table | ? | |||
aria-colspan |
Defines the number of columns spanneed by a cell or gridcell within a table | ? | |||
aria-controls |
Identifies the element (or elements) controlled by the current element |
|
|
||
aria-describedby |
Identifies the element (or elements) that describes the current element |
|
|||
aria-details |
Identifies the element that provides a detailed description of the current element | aria-details test case |
When the attribute is present, JAWS announces "Has details". When entering content that is associated as "details", JAWS will announce "Entering details." When navigating past the end of the content, JAWS will announce "Leaving". |
||
aria-dropeffect |
Indicates what actions can be performed when a dragged element is released on a drop target | Deprecated in ARIA 1.1 | |||
aria-errormessage |
Identifies the element that provides an error message for the current element | ? | |||
aria-flowto |
Identifies the next element (or elements) in an alternative reading order |
|
|||
aria-haspopup |
Indicates the availability and type of a popup menu or dialog | aria-haspup tests |
|
Works on certain roles and elements, needs thorough testing to document support. bug filed on JAWS to support the new aria-haspopup values from ARIA 1.1 | |
aria-keyshortcuts |
Indicates keyboard shortcuts provided by the author | ? | |||
aria-label |
Defines a string value that labels the current element |
|
Works on certain roles and elements, needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-labelledby |
Identifies the element that provides a label for the current element |
|
Works on certain roles and elements, needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-level |
Defines the hierarchical level of an element within a structure |
|
Works on certain roles and elements, needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-live |
Indicates that an element will be updated, and describes the types of updates |
|
Works on certain roles and elements, needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-modal |
Indicates whether an element is modal when displayed |
|
JAWS announces a dialog as modal when aria-modal="true" used in conjunction with role="dialog" |
||
aria-multiline |
Indicates whether a textbox accepts multiple lines of input, or only a single line | ? | |||
aria-multi-selectable |
Indicates that more than one item may be selected from the currently selectable descendants | ? | |||
aria-orientation |
Indicates whether the element's orientation is horizontal, vertical, or undefined | orientation test case | |
JAWS announces role=slider with aria-orientation="vertical" as "up/down slider", with aria-orientation="horizontal" as "left/right slider" |
|
aria-owns |
Identifies an element (or elements) in order to define a parent/child relationship | test-cases.tink.uk/aria-owns |
|
Works on certain roles and elements, needs thorough testing to document support. | |
aria-placeholder |
Defines a short word or hint intended to aid data entry | ? | |||
aria-posinset |
Defines an element's position in a current set of listitems or treeitems |
|
Needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-readonly |
Indicates an element is not editable, but is otherwise operable |
|
Works on certain roles and elements, needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-relevant |
Indicates what notifications the UA will trigger when the accessibility tree is modified |
|
Needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-required |
Indicates that user input is required on the current element |
|
Needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-roledescription |
Defines a human readable, author localised description for the role of an element | ? | |||
aria-rowcount |
Defines the total number of rows in a table | ? | |||
aria-rowindex |
Defines an element's row index, or position with regard to the total rows in a table | ? | |||
aria-rowspan |
Defines the number of rows spanned by a cell or gridcell | ? | |||
aria-setsize |
Defines the number of items in a current set of listitems or treeitems |
|
Needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-sort |
Indicates whether the items in a table or grid are sorted in ascending, descending order | sort test case |
|
Needs thorough testing to document support. | |
aria-valuemax |
Defines the maximum allowed value for a range |
|
Needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-valuemin |
Defines the minimum allowed value for a range |
|
Needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-valuenow |
Defines the current value for a range |
|
Needs thorough testing to document support. | ||
aria-valuetext |
Defines the human readable text of aria-valuenow |
|
Needs thorough testing to document support. |
JAWS ARIA Support Notes
Preface
Before discussing JAWS support for ARIA, it is important to understand the relationship between the ARIA markup itself, the browser in which the markup is rendered, and JAWS as it provides spoken or Braille information to users.
First, ARIA markup was designed to insert information useful to assistive technologies into existing HTML code. It exists as a way to label controls and to provide information about their states. But adding ARIA support to a Web page does not change the presentation or behavior of that Web page to sighted users. For example, adding the ARIA role of “checkbox” to a “div” tag within a Web page will produce no visible effect on the page. Instead, if there is a check box on the page which has been rendered without using the “input” tag, the ARIA role of “checkbox” can be added to the code to inform assistive technology users that a check box appears at that point on the page.
Second, the browser plays a big role in interpreting ARIA markup. Most browsers support some type of accessibility API (application programming interface), and assistive technologies use the API to get information about what is presented on the screen. So, ARIA markup is transformed by the browser into information that fits the accessibility API it supports. Then, the information provided by the API is processed by the assistive technology. That means JAWS support of ARIA depends heavily on the browser being used.
Third, JAWS gathers information from the ARIA markup and the browser’s API and presents it in a meaningful way to screen reader users. Because of the above interactions, the quality of JAWS support for ARIA markup is inextricably tied to the careful, thorough application of ARIA markup on a Web page, and comprehensive support provided by the browser in which the markup is rendered.
For best results, Freedom Scientific recommends that Web page authors read the WAI-ARIA 1.1 Authoring Practices carefully before adding ARIA markup to their pages. Also, concepts such as roles, states, landmarks, and so on are defined as part of the ARIA specification, and are therefore not defined in this document. If you are unfamiliar with these concepts please read through the ARIA documentation before continuing.
For the reasons described above, there may be differences in JAWS ARIA support between Internet Explorer and Firefox. Please test any examples in both browsers. And please specify which browser you’re using when reporting problems to Freedom Scientific.
Key Concepts
It is a good idea to have a firm grasp of the following concepts. These items form the basis of many descriptions throughout the documentation.
Virtual Cursor
JAWS presents Web pages using the JAWS Virtual Cursor. This allows users to read and navigate a Web page as though it were a text document. Users press the ARROW keys to read line by line, word by word, character by character, and so on. JAWS also provides Navigation Quick Keys, which are alpha-numeric keys that move the Virtual Cursor to features of the page such as links, headings, and form controls. In addition, users can press the TAB key to move between focusable elements on the page.
Using the ARROW keys or Navigation Quick Keys to change the position of the Virtual Cursor does not change the actual focus point in the application. This means that even if JAWS reads the text of a given link on a Web page for example, that link doesn't necessarily have the keyboard focus.
The keyboard focus is typically represented visually as a highlighted area surrounding a control.
Conversely, pressing the TAB or SHIFT+TAB key to navigate moves the focus point and the Virtual Cursor follows the focus.
Forms Mode
Because JAWS uses the arrow keys and alpha-numeric keys for Virtual Cursor navigation, these keyboard commands are not passed through to interactive controls (form fields) on the page. This approach has the added benefit of protecting users from inadvertently changing form field values or activating controls on the page while simply reviewing the content.
Forms Mode is when JAWS turns over processing of the above keys to form controls so that users can interact with them. For example, when using the Virtual Cursor, pressing the letter F moves the Virtual Cursor to the next form field on the Web page, while in Forms Mode, pressing the letter F types the character "f".
Auto Forms Mode
Before JAWS 10, JAWS users had to enter and exit Forms Mode manually. Users navigated to a given control using the Virtual Cursor, and would then press the ENTER key to activate Forms Mode. Pressing NUM PAD PLUS (PC Cursor) caused JAWS to exit forms mode.
When Forms Mode is manually activated on a given form control, focus is set to that control.
Auto Forms Mode is a feature that tells JAWS to be smart about when to enter and exit Forms Mode. This is a setting which is on by default. This approach provides a seamless experience for JAWS users when both reading and interacting with a Web page.
The behavior of Auto Forms Mode depends on the type of form field in question and the keyboard command used to navigate to it. The following is a description of the keyboard commands and how they affect Web page form fields:
ARROW Keys
When the Virtual Cursor is active, JAWS enters Forms Mode upon encountering an edit field. Focus is moved to the edit control, and users can begin typing.
In Forms Mode, the ARROW keys move the caret within the edit field. If an ARROW key is pressed and the caret has already reached the boundary of the edit field, JAWS exits forms mode and resumes using the Virtual Cursor. Pressing ESC or NUM PAD PLUS will cause JAWS to exit Forms Mode.
Edit fields are the only controls for which JAWS enters or exits Forms Mode automatically based on the ARROW keys. For other controls, if JAWS is using the Virtual Cursor, it will continue to use the Virtual Cursor. This is so that users don't accidentally change the value of a control while attempting simply to navigate past it. If JAWS is already in Forms Mode, ARROW keys will not cause JAWS to leave Forms Mode. This is so that users won't unintentionally leave Forms Mode while interacting with a control. When ARROW keys are used to navigate to non-edit controls, users must activate Forms Mode manually by pressing ENTER.
TAB Key
Using the TAB key always causes the focus point to move. When focus changes to a given form control, JAWS activates Forms Mode automatically based on the type of control in question.
For edit fields, combo boxes, spin controls, list controls, tab controls, menu bars, tree views, and grid cells, JAWS enters Forms Mode automatically.
For buttons and check boxes, JAWS exits Forms Mode.
Pressing ESC or NUM PAD PLUS will cause JAWS to exit Forms Mode if it is active.
It is possible to move to a form field by using TAB and to move away from that form field using the ARROW keys, and vice versa.
Different Control Types
In terms of Forms Mode, there are two groups of controls: those that require Forms Mode to interact with them, and those controls that never require Forms Mode to interact with them.
Forms Mode is required for edit fields, combo boxes, spin controls, list controls, tab controls, menu bars, tree views, and grid cells. For these controls, press ENTER or SPACEBAR to enter Forms Mode, and ESC or NUM PAD PLUS to exit Forms Mode.
For buttons and check boxes, use ENTER or SPACEBAR to activate the control at the location of the Virtual Cursor. Users interact with these controls simply by pressing ENTER or SPACEBAR; so forms mode is unnecessary. Auto Forms Mode causes JAWS to leave Forms Mode when it encounters these control types because they are just as usable without Forms Mode.
For combo boxes only, ALT+DOWN ARROW causes JAWS to enter Forms Mode and drop down the list of combo box items. ALT+UP ARROW closes the list of combo box items and causes JAWS to exit Forms Mode.
Finally, JAWS Auto Forms Mode behavior for radio buttons is a little different from its behavior with other types of controls. This is because unlike other controls, it is possible to interact with radio buttons in both Forms Mode and with the Virtual Cursor. When navigating with the TAB key, JAWS will stay in Forms Mode if it is already on, and it will not enter Forms Mode if it is off. Users can press SPACEBAR to choose a specific radio button when using the Virtual Cursor, and pressing the ARROW keys will not change the value of the radio button group. Users can also press ENTER to activate Forms Mode, and subsequent presses of the UP and DOWN ARROW keys will change the value of the radio button group. The following table contains the expected behavior for radio buttons with Auto Forms Mode.
